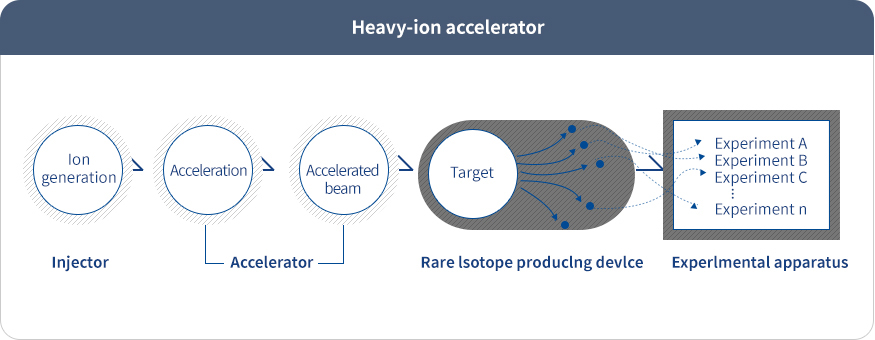
An accelerator is a device that accelerates particles with electric charges, such as electrons, protons and ions. Depending on the accelerated particle and the purpose of utilization, accelerators can be classified into synchrotron accelerators, proton accelerators, baryon accelerator, and heavy-ion accelerators. Among these accelerators, heavy-ion accelerators are used to produce rare isotopes that have not been observed in nature.
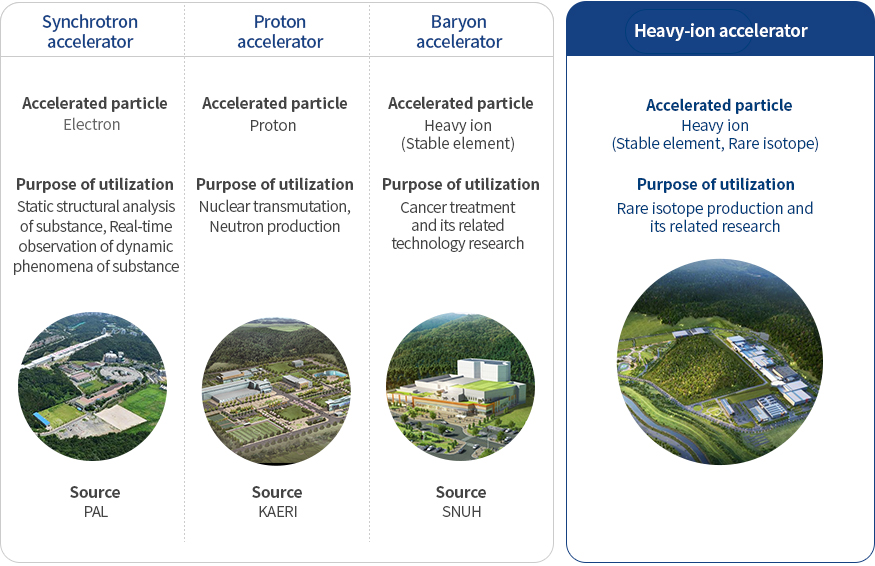
Synchrotron accelerator : Accelerated particle-Electron, Purpose of utilization-Static structural analysis of substance, Real-time observation of dynamic phenomena of substance(Photo Source - PAL)
Proton accelerator : Accelerated-Proton, Purpose of utilization-Nuclear transmutation, Neutron production(Photo Source - KAERI)
Baryon accelerator : Accelerated-Heavy ion (Stable element), Purpose of utilization-Cancer treatment and its related technology research(Photo Source - SNUH)
Heavy-ion accelerator : Accelerated-Heavy ion(Stable element, Rare isotope), Purpose of utilization-Rare isotope production and its related research
Heavy-ion accelerators ionize atoms heavier than hydrogen and helium, and cause them to collide with target atoms. Such collisions unlock physics on a scale smaller than atoms, leading to the discovery of new, rare isotopes.