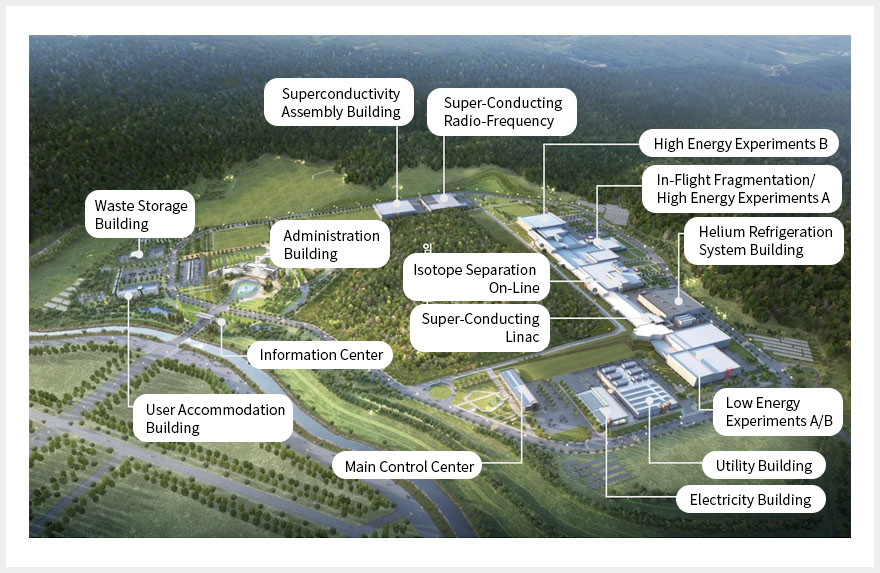
Goal
* RAON - Rare isotope Accelerator complex for ON-line experiments
Period
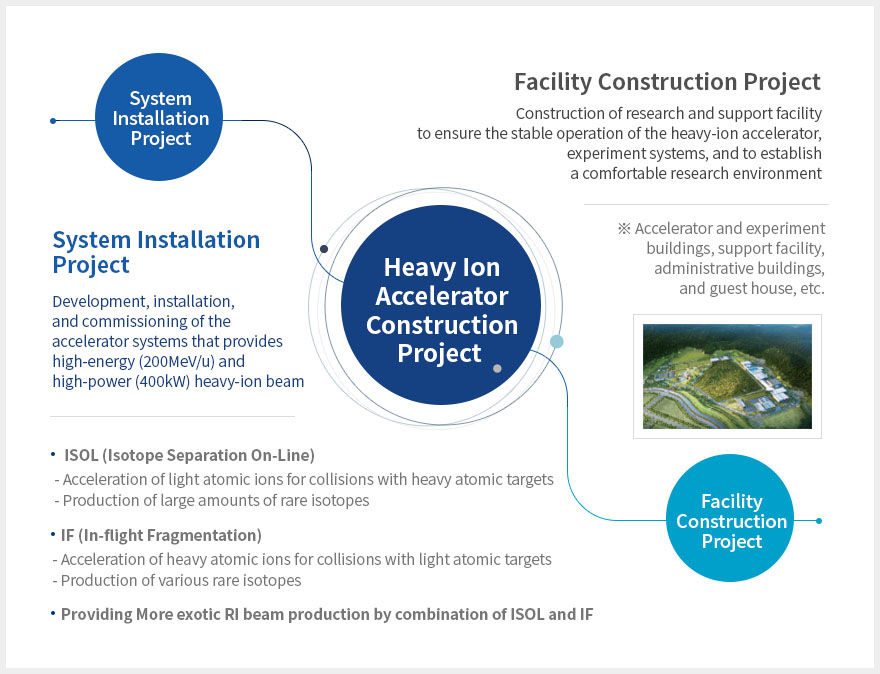
Budget
- accelerators and experimental apparatus : 522.8 billion won
- civil engineering & conventional facilities : 996 billion won (incl. site 357 billion won)
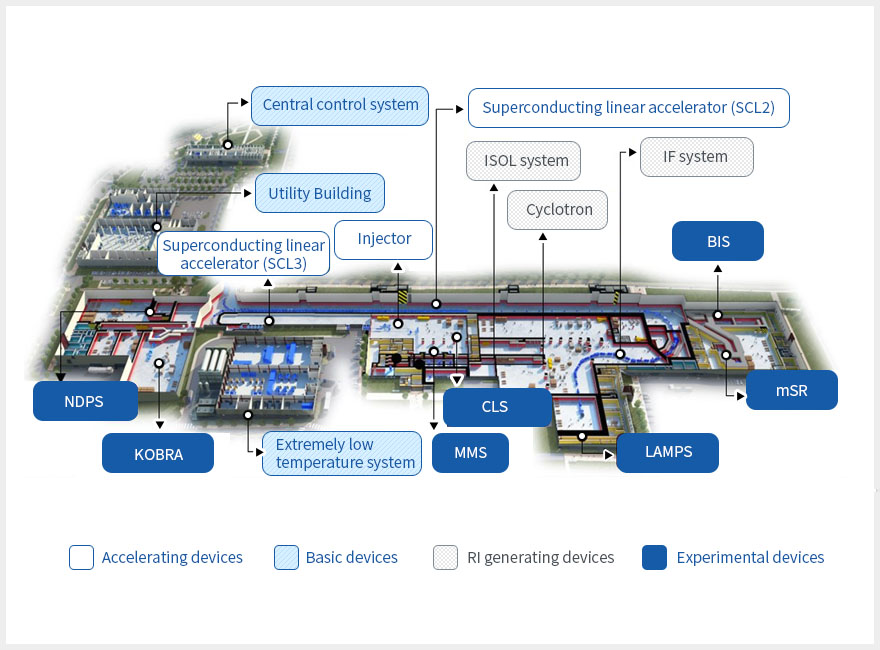
| Term | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| Accelerating devices | Injector | Used to generate heavy ions and deliver them to the superconducting linear accelerators |
| Superconducting linear accelerator (SCL3) | Used to accelerate heavy ions and RI beams delivered by the injector to 18.5MeV/u (in the case of uranium) | |
| Superconducting linear accelerator (SCL2) | Used to accelerate heavy ions and RI beams of 18.5MeV/u to 200MeV/u (in the case of uranium) | |
| Basic devices | Central control system | Designed to synchronize major components of the heavy ion accelerator, provide visual information, detect and correct errors of different devices, and interconnect various systems operated in a distributed environment |
| Extremely low temperature system | Designed to supply helium generated at the extremely-low-temperature plant to the superconducting linear accelerators (SCL3 and SCL 2) to maintain the extremely-low-temperature environment | |
| RI generating devices | ISOL system | Designed to accelerate light ions (protons, etc.) to collide into heavy targets (uranium, etc.) to generate rare isotopes |
| IF system | Designed to accelerate heavy ions (uranium, etc.) to collide into light targets (carbon, etc.) and generate rare isotopes | |
| Experimental devices | Super-low energy experimental device | Used to measure the basic physical quantities of the atomic nucleus of a rare isotope in the super-low-energy field (0.1MeV or lower) |
| Low-energy experimental device | Used to explore the unique structure of the atomic nucleus and the principles of the generation of elements and measure nuclear data, etc., in the low-energy field (up to 18.5MeV/u in the case of uranium) | |
| High-energy experimental device | Used to explore the state of the atomic nucleus in extreme conditions and study material science and biomedical science in the high-energy field (18.5MeV/u-200MeV/u in the case of uranium) | |